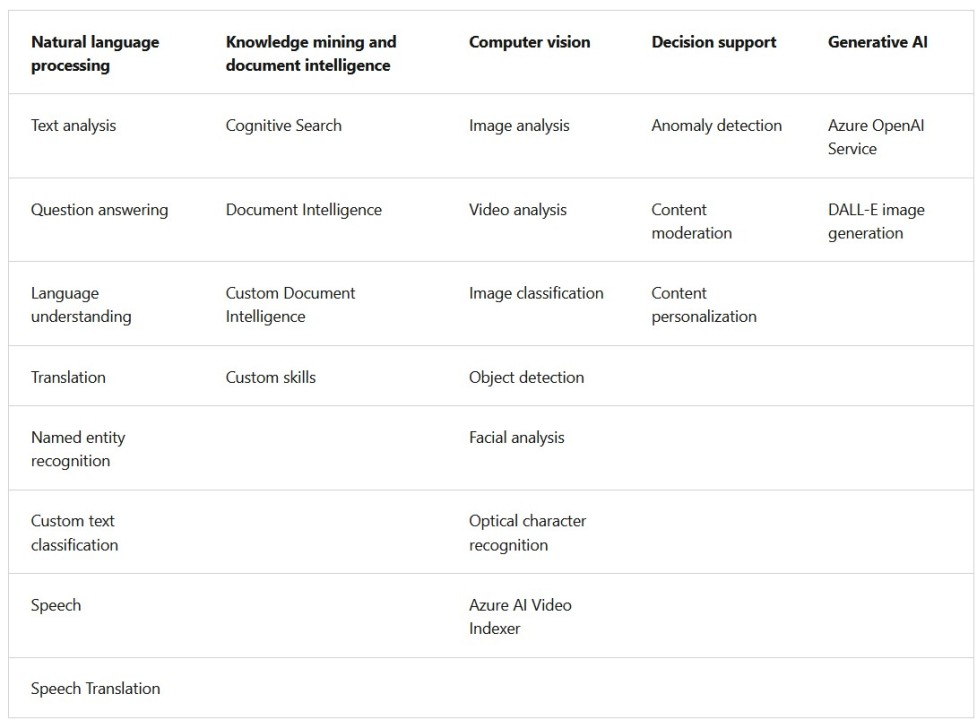
Natural Language Processing (NLP):

What it is: Natural Language Processing (NLP) is an area of artificial intelligence that deals with the interaction between computers and humans using natural language. This involves the understanding, interpretation, and generation of human language by computers.
How it works: NLP allows machines to understand the context, meaning, and intention behind text or speech. This involves tasks such as sentiment analysis, language translation, text summarization, information extraction from documents, among others.
Applications: Chatbots, virtual assistants, recommendation systems, sentiment analysis on social media, automatic translation, text summarization, among others.
Knowledge Discovery and Document Information:

What it is: Knowledge Discovery and Document Information (or KDD – Knowledge Discovery in Databases) refers to the process of discovering and extracting useful information, patterns, and hidden knowledge from large volumes of unstructured data.
How it works: This process involves steps like data pre-processing, cleaning, transformation, mining, and interpretation of data. Machine learning algorithms and statistical techniques are used to identify patterns, trends, and hidden relationships in the data.
Applications: Text analysis, document classification, fraud detection, recommendation systems, pattern recognition in large datasets.
Visual Computing:

What it is: Visual Computing focuses on the analysis, interpretation, and understanding of images and videos by computational systems.
How it works: It uses algorithms and techniques to extract useful information from visual data, such as object recognition, face detection, image segmentation, motion tracking, among others.
Applications: Facial recognition, autonomous vehicles, medical diagnosis through imaging, security monitoring through cameras, augmented reality, among others.
Decision Support:

What it is: Decision Support in AI refers to the use of intelligent systems to assist humans or automate decision-making processes.
How it works: It uses models, algorithms, and data to provide insights and recommendations that aid decision-making. It can involve expert systems, machine learning, and data analysis techniques.
Applications: Recommendation systems, financial risk analysis, computer-aided medical diagnosis, demand forecasting, among others.
Generative AI:

What it is: Generative AI refers to models and systems capable of creating new and original content, such as images, music, text, based on patterns learned from large datasets.
How it works: It uses techniques like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) to generate synthetic data that resembles real data, enabling the creation of authentic content.
Applications: Generating realistic images, creating music and art, text synthesis and natural language, among other creative content generation areas.
These AI services have applications in various sectors, from improving human-computer interaction to assisting in complex processes of analysis, interpretation, and information creation.
Okay, okay, it got too theoretical, right? Let’s move on to real-world applications:
Natural Language Processing (NLP):
- Text Analysis:
Utility: Text analysis is essential for extracting insights from large volumes of textual data. It identifies sentiments, main themes, patterns, and trends in texts, whether on social networks, product reviews, or customer feedback.
Real world: Companies use text analysis to monitor social networks and understand how consumers feel about their products or services. This helps in reputation management and identifying areas for improvement.
- Question Answering:
Utility: Systems capable of answering questions are useful in various contexts, from virtual assistants to customer support tools. These systems can interpret questions in natural language and provide accurate answers based on available data.
Real world: Customer support chatbots that can answer common user questions, such as information about products, return policies, or basic technical assistance.
- Speech Recognition:
Utility: Speech recognition is used to transcribe human speech into text. This enables interaction with devices via voice, such as virtual assistants or dictation systems.
Real world: Personal assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant use speech recognition to understand voice commands and perform actions like setting reminders, making calls, or playing music.
- Translation:
Utility: Automatic translation is essential for global communication, allowing people to overcome language barriers by translating text from one language to another in real-time.
Real world: Platforms like Google Translate or real-time translation services in video calls help translate conversations between people speaking different languages.
- Named Entity Recognition:
Utility: Identifies and classifies specific information such as names of people, places, organizations, dates, quantities, among others, within a text.
Real world: In news analysis, named entity recognition can help identify protagonists, locations, and relevant dates in journalistic articles.
- Custom Text Classification:
Utility: Allows text categorization according to specific criteria, such as sentiment analysis, spam detection, email sorting, among others.
Real world: Companies use text classification to filter unwanted emails (spam) or to classify customer feedback into positive, negative, or neutral for further analysis.
- Speech:
Utility: It is the ability to understand and generate human speech. This is used in speech synthesis systems to generate voice from text and in speech recognition to transcribe human speech into text.
Real world: Navigation assistants in cars use speech recognition to allow drivers to give voice commands for navigation, calls, or music playback safely.
These NLP applications have transformed how we interact with technology, improving efficiency, personalization, and accessibility in a variety of contexts.
Knowledge Discovery and Document Information:
- Cognitive Search:
Utility: Cognitive Search is an advanced search approach that uses AI to understand document content. It goes beyond simple keyword search, analyzing and interpreting document context.
Real world: This technology is used in enterprise search platforms, digital libraries, and information portals to enable more precise and contextual searches. It improves result relevance by considering the meaning and context of documents, resulting in a smarter and more efficient search experience.
- Document Intelligence:
Utility: Document Intelligence refers to the ability to extract valuable and structured information from unstructured documents such as PDFs, images, emails, and text files.
Real world: This technology is used in document automation processes, contract analysis, record management, and large-scale information extraction. It allows companies to process large volumes of documents efficiently, identifying key information and converting unstructured data into usable data.
- Personalized Document Information:
Utility: This approach focuses on providing specific and personalized information from documents, adapting to individual user needs and preferences.
Real world: In content management systems and digital libraries, personalized document information allows more accurate recommendations of documents based on the interests and behaviors of specific users. It is used to personalize information portals, allowing users to access relevant content more effectively.
- Custom Abilities:
Utility: These are functionalities and capabilities tailored to the needs and specifics of a particular environment or user.
Real world: In contexts such as virtual assistants or information management systems, custom abilities allow systems to be tailored to meet the specific needs of a company, user, or scenario. For example, in a corporate environment, custom abilities may include specific process automations, integration with existing systems, and responses to specific questions related to a domain or sector.
Visual Computing:
- Image Analysis:
Utility: Image analysis involves extracting information, patterns, and visual characteristics from an image.
Real world Applications: Widely used in pattern recognition, medical diagnostics through imaging, quality inspection on production lines, object recognition, and detection of specific visual events.
- Video Analysis:
Utility: Involves interpreting sequences of video frames to extract meaningful information.
Real world Applications: Used in video surveillance to detect suspicious activities, analyze movements and interactions in behavioral studies, traffic monitoring, among others.
- Image Classification:
Utility: Consists of assigning a category or label to an image based on its visual characteristics.
Real world Applications: In image recognition systems, it is used to categorize images into specific categories, such as identifying dog breeds, types of flowers, car models, among others.
- Object Detection:
Utility: Identification and localization of specific objects within an image or video.
Real world Applications: Widely used in security systems to detect intruders, in autonomous vehicles to identify pedestrians and obstacles, in monitoring systems to identify specific items in an environment.
- Facial Analysis:
Utility: Recognizes and analyzes facial characteristics to identify individuals or emotional patterns.
Real world Applications: Used in security systems for facial recognition on mobile devices, in access control systems, facial expression analysis for sentiment assessment in market research, among others.
- Optical Character Recognition (OCR):
Utility: Converts text contained in images or scanned documents into editable text.
Real world Applications: Used for document scanning, vehicle license plate recognition, extraction of information from receipts in expense apps, among others.
- Azure AI Video Indexer:
Utility: It is an AI-based video analysis platform that offers features such as audio transcription, facial recognition, object detection, and video content indexing.
Real world Applications: Used in media management systems, in the entertainment industry to catalog video content, in companies for analyzing customer video feedback, among other applications.
Decision Support
- Anomaly Detection:
Utility: Identification of unusual or outlier patterns in data.
Real world Applications: Used in security systems to detect suspicious activities, in computer networks to identify malicious behaviors, in healthcare to detect anomalies in patient vital signs, and in manufacturing systems to identify equipment failures.
- Content Moderation:
Utility: The process of monitoring and removing inappropriate, illegal, or offensive content.
Real world Applications: Used on social media platforms to remove inappropriate content, in online forums to filter offensive language, in corporate environments to ensure compliance with digital resource usage policies.
- Content Personalization:
Utility: Adapting information and experiences based on user preferences and interaction history.
Real world Applications: In streaming services for movie and music recommendations based on viewing history, in online stores to recommend products based on previous purchases, in news portals to display user-interest content.
Generative AI: focuses on creating authentic and new content.
- Azure OpenAI Service:
Utility: The Azure OpenAI service is a platform that provides access to powerful AI models, including generative language models like OpenAI’s Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT). These models can generate text, understand natural language, and perform language processing tasks.
Real world Applications: Used in virtual assistants, customer service chatbots, automatic email responses, text translation, document summarization, among others. These models are trained to understand and generate textual content based on large datasets, improving efficiency and interaction with users.
- DALL-E Image Generation:
Utility: DALL-E is an image generative model from OpenAI capable of creating images from textual descriptions. It generates images based on input text, creating visual representations of described concepts.
Real world Applications: Can be applied in graphic design, art creation, generation of illustrations, visual prototypes, among others. This technology enables the generation of customized images based on descriptions, facilitating the visualization of concepts or ideas before actual production.
Hope it helps. Happy studying!!!